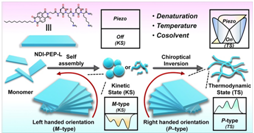
Peptide-based tunable piezoresponsive nanomaterials have emerged as an important area of research
Peptides, as short chains of amino acids, exhibit remarkable flexibility in design, allowing for the creation of nanomaterials with tailored properties. This tunability is particularly beneficial in piezoresponsive systems, where the material’s electrical response changes in relation to applied mechanical stress. By leveraging the inherent responsiveness of peptides, researchers have formulated nanomaterials that can convert mechanical energy from ambient vibrations or body movements into electrical energy, thus serving as efficient energy harvesters. Such systems can power wearable devices, sensors, and other portable electronics, reducing reliance on traditional power sources.
In addition to energy harvesting, peptide-based nanomaterials possess noteworthy advantages for biodevice applications. Their biocompatibility ensures safe interaction with biological systems, while their ability to be engineered for specific functionalities opens avenues for their use in drug delivery, biosensing, and tissue engineering. For example, piezoresponsive nanomaterials can be integrated into biosensors that monitor physiological changes in real time, enhancing diagnostics and patient care.
Moreover, the environmental sustainability of peptide-based materials further underscores their significance in current technological landscapes. Derived from renewable biological sources, these nanomaterials present a greener alternative to conventional inorganic materials, aligning with global efforts toward sustainable development.
In conclusion, peptide-based tunable piezoresponsive nanomaterials stand at the forefront of innovation in energy harvesting and biodevice applications. Their exceptional properties combine biocompatibility with mechanical responsiveness, paving the way for advanced technologies that are both efficient and environmentally friendly. As research in this domain progresses, the potential for practical applications continues to expand, heralding a new era of smart materials that may profoundly impact energy and healthcare industries.